One connection, many advantages
White Paper: Single Pair Ethernet for Device Manufacturers
One connection, many advantages
White Paper: Single Pair Ethernet for Device Manufacturers
We would like to thank Weidmüller for producing this white paper.

Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) is a breakthrough technology that is revolutionizing Ethernet communication. What advantages, opportunities and possibilities does it hold for device manufacturers? This white paper addresses exactly these questions – and of course delivers the insights you need.
Outline
- How does Single Pair Ethernet work?
- What SPE standards and specifications are currently available?
- What are the benefits of SPE for device manufacturers?
- What prospects do SPE applications offer device manufacturers?
- What should be considered when designing SPE devices?
- What are the future trends and developments?
- Conclusions and key-takeaways
1. How does Single Pair Ethernet work?
Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) is a breakthrough technology that simplifies Ethernet communication by using a single twisted pair of wires instead of the traditional two or four pairs. This approach supports high-speed data transmission rates over long distances, multidrop applications, and can additionally deliver power via the same pair of wires. SPE is particularly beneficial for applications where weight, space and cost are important, making it ideal for both industrial and commercial use.

Key Benefits of SPE
- Improved data transfer:
SPE enables high-speed data transmission over long distances, ensuring fast and reliable communication. This is crucial for real-time data processing and control across various applications. Additionally, SPE supports multidrop configurations, allowing multiple devices to share a single communication line.
- Simplified Network Architecture:
By reducing the complexity of the network architecture, SPE simplifies network management and maintenance. It allows Ethernet connectivity to reach sensors and field devices directly, minimizing the need for gateways and intermediary components.
- Power over data line (PoDL):
SPE’s capability to transmit both power and data over a single twisted pair of wires eliminates the need for separate power lines. This is particularly useful for supplying power to remote sensors, actuators, and IoT devices.
- Efficient installation:
Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) significantly reduces the amount of cabling required, leading to lower material and installation costs. This efficiency is especially valuable in environments with extensive wiring needs, such as manufacturing facilities and large commercial buildings.
2. What SPE standards and specifications are currently available?
Single Pair Ethernet standards refer to a set of guidelines and specifications established for using Ethernet technology over a single pair of twisted copper wires. These include all aspects of SPE, such as Ethernet interfaces, cabling and data transmission. The standard for SPE is defined as IEEE 802.3. This specification outlines the technical parameters for Ethernet-based data communication over a single pair of cables.
The following table gives an overview of the different SPE protocols. These standards differ in their transmission speeds and distances, ensuring interoperability and providing guidelines for developing compliant products.
Overview of IEEE802.3 SPE protocols
Further SPE standards in progress – forecast 2025
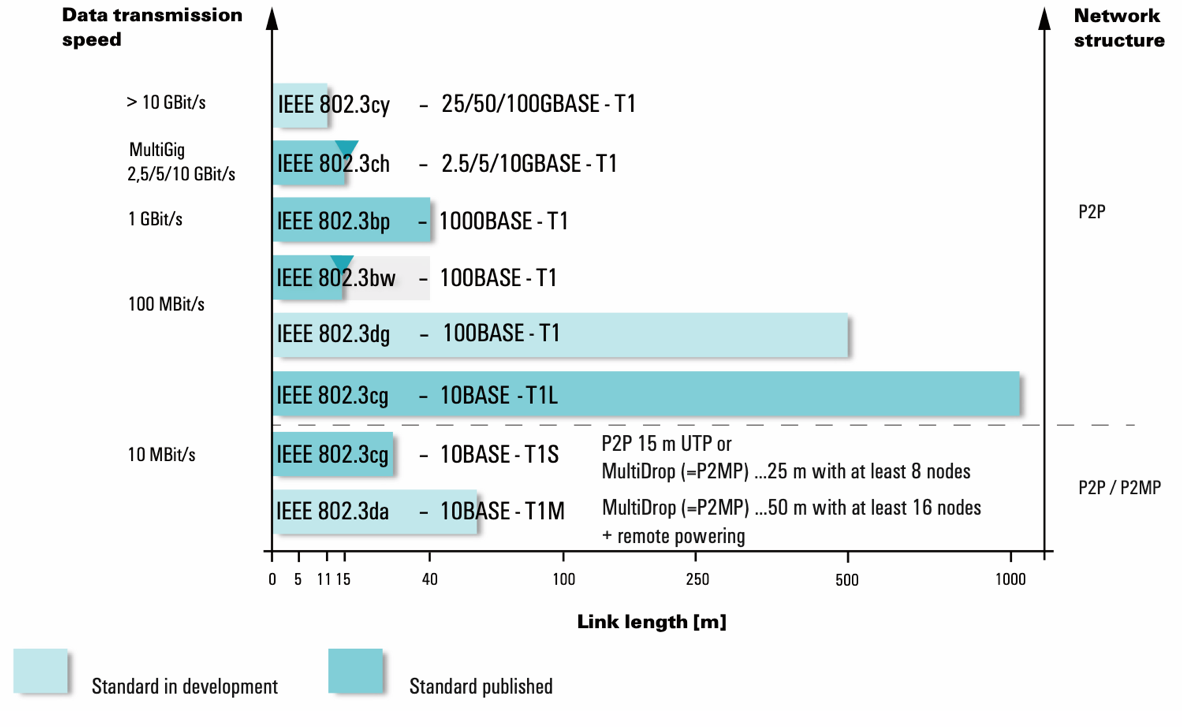
The most important standards for the industry at present include 10BASE-T1L, which supports transmission speeds of 10 Mbit/s over cable lengths of up to 1,000 meters, and 10BASE-T1S, which is designed for multidrop applications. 100BASE-T1 enables 100 Mbit/s over distances up to 100 meters, while 1000BASE-T1 supports 1 Gbit/s over distances up to 40 meters. Once available, 100BASE-T1L (IEEE 802.3dg) is also expected to become highly relevant for industrial applications.
The IEC 63171 standard addresses the standardization of connection technology and requirements for SPE connectors. It defines electrical and transmission characteristics as well as various mating face types. Additionally, the MICE concept (Mechanical, Ingress, Climatic, and Electromagnetic) is integrated into the standard, covering environmental conditions and application areas.
Recently, international automation communities have emphasized the need for a standardized connector for Single Pair Ethernet. A proposal has been submitted for international standardization based on essential application requirements. With the adoption of a uniform mating face for SPE, the industry is taking a significant step toward a more unified and future-ready connectivity landscape. The new SPE connector system provides a consistent interface for use in control cabinets, field installations, and hybrid environments. Numerous manufacturers have already announced plans to implement this standard. As a key driver of this technology, Weidmüller will also expand its product portfolio to include connectors based on the IEC 63171-7 standard, aligning with the new design.

3. What are the benefits of SPE for device manufacturers?
Industrial equipment manufacturers are responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, from R&D to prototype design and manufacturing to production, quality control and sales. They must comply with industry standards and regulations and ensure that their products are safe, reliable, and meet the requirements of their customers.
Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) is rapidly emerging as an industry standard, and its widespread adoption is increasingly expected by customers. As more devices and networks begin to rely on SPE, now is the ideal time to consider integrating this technology into the next generation of products. Designing devices with a single pair of wires offers several advantages—particularly when compactness and weight reduction are key. This makes SPE especially valuable in applications where space and weight are critical factors. Compared to a standard RJ45 jack, the SPE connector significantly reduces the required PCB footprint, enabling more efficient and flexible device designs.
At the same time, SPE enables direct access to the field level, even over long distances. By connecting different sensors via SPE at a great distance, the information is available directly via the IIoT without the need for additional gateways. This enables diagnostic capabilities that contribute to increased system availability.
Single Pair Ethernet serves as an additional physical layer that enables seamless communication using Ethernet-based protocols such as Modbus TCP, PROFINET, Ethernet/IP, and HTTP. This provides a versatile solution for a wide range of applications. By supporting existing Ethernet protocols, SPE ensures easy integration into current network infrastructures. As a result, adopting SPE can simplify network design. Devices based on SPE also offer enhanced performance and reliability. Leveraging Ethernet’s robust and fast data transmission capabilities, these devices outperform traditional fieldbus systems in both speed and dependability.
In addition, SPE enhances versatility and cost-effectiveness. Its ability to transmit both data and power over a single pair of cables simplifies the design of devices for various environments, from industrial settings to smart buildings. SPE helps reduce production costs by minimizing material usage and streamlining manufacturing processes. The reduced need for multiple connectors and cables makes products more economical overall. By requiring fewer cable and connector types, warehousing and logistics are simplified, reducing operational effort and easing supply chain management.
Moreover, the introduction of SPE enables equipment manufacturers to future-proof their products. As SPE becomes more widespread, compatible devices remain relevant in the market and are better aligned with emerging industry standards and trends.
Finally, SPE supports sustainability by reducing the amount of cables and materials required. Lighter cables lower transport emissions and energy consumption during installation, contributing to a more environmentally friendly manufacturing process.
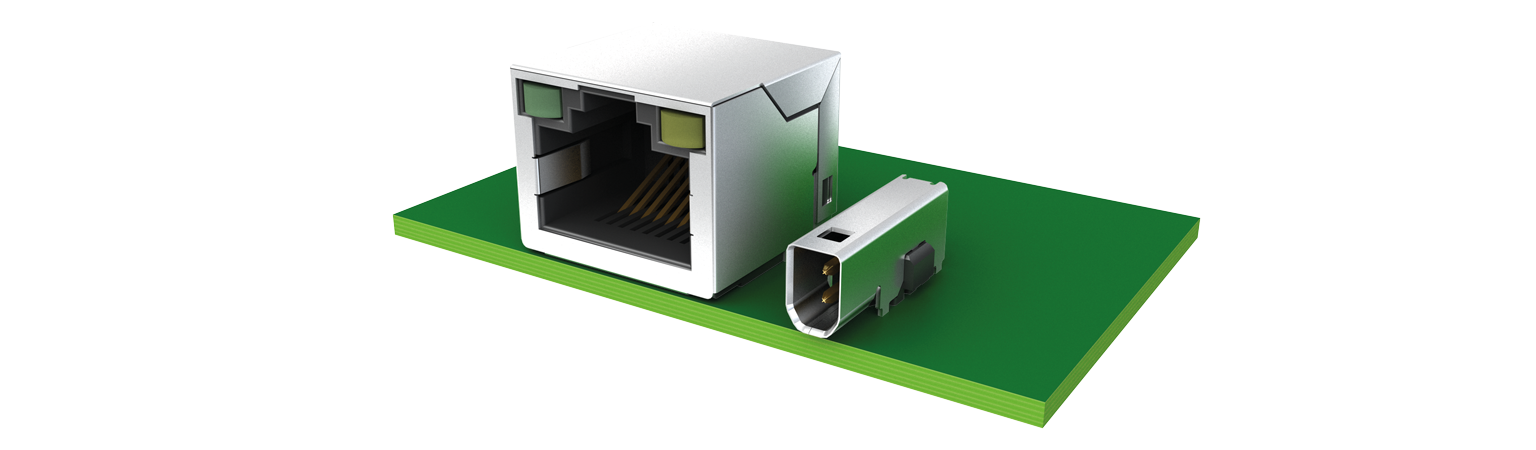
4. What prospects do SPE applications offer device manufacturers?
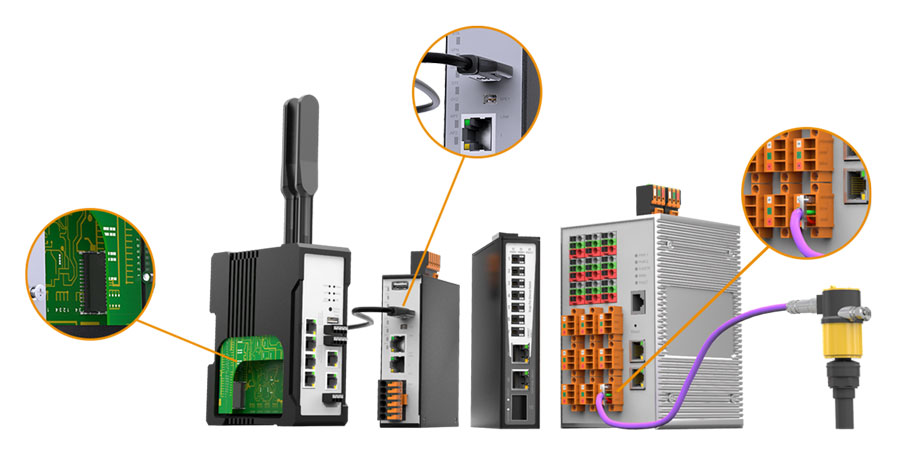
As automation advances, an increasing number of sensors and actuators are being deployed across all areas of manufacturing. Connecting IIoT devices to the cloud requires a consistent, scalable, and low-latency network built on reliable components. SPE enables Ethernet connectivity across all automation levels, down to individual sensors and actuators.
SPE is particularly useful in environments where smart devices communicate, measure, or monitor. Typical applications include barcode readers, cameras, user terminals, and various detection sensors. In industrial automation, long distances of up to 1,000 meters must be bridged at high transmission speeds—without the need for additional gateways. The many sensors, actuators, and field devices in factories also require a power supply. Thanks to PoDL (Power over Data Line), both power and data can be transmitted simultaneously over the same pair of wires, eliminating the need for separate power lines.
Single Pair Ethernet offers significant advancements in the miniaturization of communication infrastructure and enables the development of sophisticated end-of-arm tools for robots. Unlike traditional protocols, SPE provides greater bandwidth, allowing communication between a robotic arm and its controller to support larger data frames.
SPE supports high-resolution 2D and 3D systems by enabling data transmission at speeds of up to 1 Gbps over distances of up to 40 meters. Additionally, SPE cables have a smaller bending radius compared to traditional automation cables, which can help reduce the overall dimensions of the robot body and arm. This compact design is particularly beneficial in robotics.

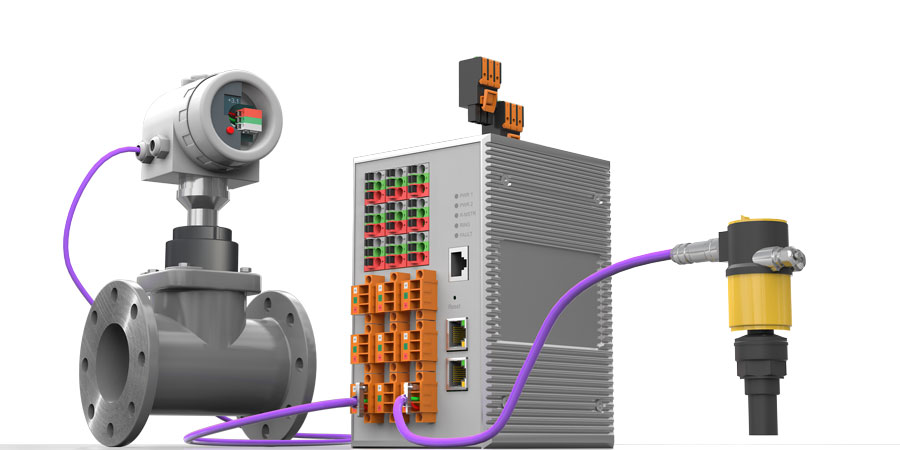
In the process industry, Ethernet-compatible interfaces are increasingly required to access field-level data via IIoT. The challenge lies in retrieving information from sensors and devices located at significant distances, while also integrating various IIoT devices into the network infrastructure.
Single Pair Ethernet for the process industry is known as Ethernet-APL, a specialized version of the 10BASE-T1L standard enhanced with functional safety features. It enables qualified components to transmit data at 10 Mbit/s while simultaneously supplying power over twisted-pair cables up to 1,000 meters in length.
Ethernet-APL (Advanced Physical Layer) technology allows direct access to field and device levels through an internationally standardized two-wire solution. This requires high-performance IIoT devices built with quality components. The result is increased plant availability and improved data generation: device data can be collected, utilized, and analyzed directly in the field to optimize operations and implement innovative solutions.
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) into building automation has become a key element of digital transformation and is expected to grow in importance. The introduction of the IP protocol simplifies building automation and increases its efficiency, as sensors, controllers, and other building technologies can be seamlessly connected to building systems—even over long distances. This approach replaces conventional proprietary fieldbus systems with standardized Ethernet cabling, eliminating the need for costly and time-consuming programming. With Single Pair Ethernet (SPE), additional gateways are no longer required.
In the design and development of smart buildings, there is a clear trend toward minimizing the energy consumption of all connected devices. SPE plays a crucial role in this context by enabling the simultaneous transmission of high-performance data and power over a single pair of wires using Power over Data Line (PoDL). Additionally, SPE components—including connectors and cables—are designed to be both durable and efficient. SPE allows for the seamless integration of building systems such as lighting and HVAC.
It also ensures security within a unified network that is easy to install and maintain. The ability to support various transmission distances and data rates, combined with high packing density, makes this interconnect technology highly adaptable to nearly any system. SPE is transformative for IoT device connectivity, which is essential for applications such as smart grids, smart cities, and building automation.

Thanks to its ability to transmit data over longer distances than traditional Ethernet—such as 10BASE-T1L, which supports 10 Mbps over up to 1,000 meters—Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) is also well-suited for large infrastructure projects like tunnels and level crossings, where long range and reliable data rates are essential. It can be used for signal control, power supply, sensing, connectivity, and drive control. For large-scale installations such as trackside systems along railway lines and traffic control networks, SPE simplifies complex cabling requirements.
By delivering both power and data through a single pair of wires, SPE streamlines the installation and maintenance of equipment such as sensors and cameras in traffic control and monitoring systems. Its compatibility with existing Ethernet-based systems ensures seamless integration and enables real-time data exchange and monitoring. Additionally, SPE’s scalability makes it ideal for expanding existing infrastructure projects. It can easily accommodate growing data demands and the integration of new devices—without requiring major changes to the existing setup.
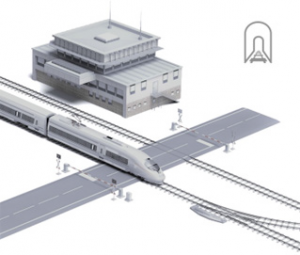
Single Pair Ethernet also offers numerous advantages for the energy sector. Its ability to support high-speed data communication over long distances makes it ideal for monitoring and controlling remote energy assets such as wind turbines, solar farms, and substations. With Power over Data Line (PoDL), SPE simplifies the deployment of smart grid devices, sensors, and actuators, and facilitates the integration of IoT technologies. In addition, real-time data exchange and monitoring enabled by SPE are crucial for efficient energy management, predictive maintenance, and ensuring the stability and reliability of the power grid.


5. What should be considered when designing SPE devices?
When developing SPE-compatible products, manufacturers should consider several key aspects related to components, compliance, testing, and system architecture.
In terms of connector design, it’s important to note that SPE connectors are smaller and simpler than traditional Ethernet connectors, helping reduce both size and cost. These connectors must be designed for robustness and reliability, tailored to the specific application environment. The IEC 63171 standard defines various connector types, enabling the use of standardized components in device development. For manufacturers needing to transmit power, signal, and data, hybrid connectors can play a crucial role. A good example is Weidmüller’s OMNIMATE® 4.0, which offers a compact and convenient solution for such transmission needs.
Regarding cabling, SPE-specific cables are optimized to support high data rates and power transmission over longer distances, while minimizing interference and signal loss. They also allow for a reduced bending radius, which can be a significant advantage in equipment design.
Selecting the appropriate physical layers (PHYs) and transceivers that comply with SPE standards is essential for converting digital data into the electrical signals required for transmission. Ethernet controllers must also support SPE to ensure efficient traffic management and compatibility with the necessary protocols.
Integrating SPE into the network infrastructure requires compatible components such as switches and routers. For 10BASE-T1L applications, Weidmüller offers a switch that meets all SPE requirements. These infrastructure components must support SPE to ensure seamless integration and efficient data routing.
Manufacturers must also choose suitable chipsets and decide whether to implement Power over Data Line (PoDL). If PoDL is used, the appropriate classification must be considered, and effective energy management becomes critical. Devices should be designed to handle both data and power transmission efficiently.
EMI and EMC compliance is another important factor. Ensuring resistance to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and maintaining electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is vital, especially in industrial environments where electrical noise is common.
Finally, testing and certification of devices and components is essential. Compliance with SPE standards and obtaining the appropriate certifications ensures interoperability and reliability. Rigorous testing validates performance under various conditions and helps guarantee long-term functionality.
6. What are the future trends and developments?
The adoption of Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) is poised for significant growth as more industries recognize its numerous benefits. In the future, we can expect higher data rates, enhanced power capabilities, and further miniaturization of connectors and components—making SPE an increasingly attractive solution for demanding applications. As the ecosystem of SPE-compliant devices continues to expand, a surge in innovation and new opportunities for device manufacturers is anticipated.
This growing ecosystem will not only enhance existing technologies but also pave the way for groundbreaking applications. By leveraging the advantages of SPE, industries can gain a competitive edge in an increasingly connected and technologically advanced world. As SPE technology continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play a crucial role across a wide range of applications—from automotive networks and industrial automation to the process industry, building automation, IoT applications, and smart grids.
SPE is a key enabler of the next generation of connected devices, driving innovation and unlocking new capabilities.

7. Conclusions and key-takeaways
Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) represents a significant advancement in Ethernet technology and is set to transform networking across a wide range of industries. It offers numerous advantages, particularly for equipment manufacturers.
In industrial automation and process industries, the ability to transmit high-speed data and power over long distances is especially beneficial. SPE enables the creation of smarter, more responsive industrial networks and supports real-time data monitoring and control from remote sensors. This leads to optimized production processes and increased operational efficiency.
In building automation, SPE facilitates the deployment of smart technologies such as advanced HVAC systems, lighting controls, and security systems—all of which benefit from improved connectivity and enhanced data processing capabilities.
By significantly reducing cabling complexity, SPE not only lowers material costs but also simplifies installation and maintenance—critical factors for large-scale implementations like industrial and building management systems. Device manufacturers that adopt SPE will be well-positioned to leverage these benefits and lead the development of the next generation of connected devices.
The enhanced data transmission capabilities, combined with integrated power delivery via Power over Data Line (PoDL), make SPE an ideal solution for the expanding Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. This integration allows devices to be powered and connected through a single twisted pair of wires, simplifying design and minimizing the physical footprint of interconnect infrastructure. As the number of IoT devices continues to grow, the demand for efficient, compact, and reliable connectivity solutions like SPE is increasing.
For equipment manufacturers, the introduction of SPE technology opens new opportunities for innovation and competitiveness. Its scalability and compatibility with existing Ethernet standards enable the development of more efficient, easier-to-deploy, and future-proof products. This ensures seamless integration into both current and future network environments, providing a strong foundation for long-term technological progress.
In summary, Single Pair Ethernet is a groundbreaking development in Ethernet technology that delivers significant benefits to both device manufacturers and end users. Its ability to simplify cabling, enhance data transmission, and integrate power supply makes it a key enabler for the future of industrial automation, building automation, and IoT applications. Manufacturers that embrace SPE will be at the forefront of innovation, driving the creation of smarter, more efficient, and more powerful devices than ever before.
Here you can download and share the whitepaper.
Send a friend